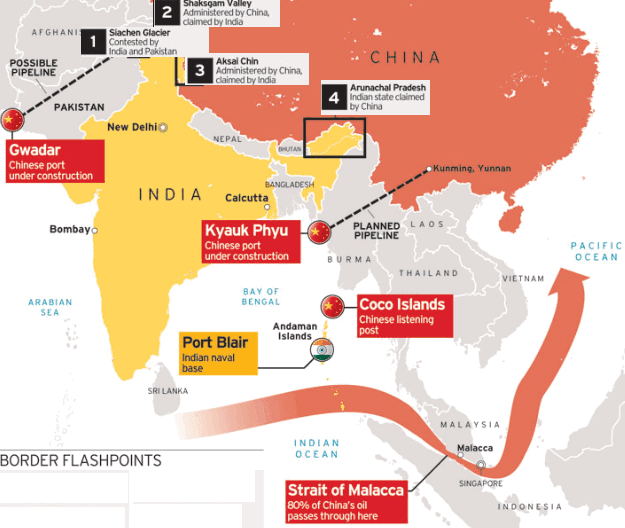
KASHMIR CONFLICT is a territorial dispute between INDIA , PAKISTAN and
The KASHMIRI INSURGENT GROUP over the control of the Kashmir Region.

The Kashmir dispute dates from 1947. The partition of the Indian sub-continent along religious lines led to the formation of India and Pakistan. However, there remained the problem of over 650 states, run by princes, existing within the two newly independent countries.

Maharaja Hari Singh signed the Instrument of Accession in October 1947 under which he acceded the State of Jammu and Kashmir to the Union of India.
But his hopes of remaining independent were dashed in October 1947, as Pakistan sent in Muslim tribesmen who were knocking at the gates of the capital Srinagar.
Hari Singh appealed to the Indian government for military assistance and fled to India. He signed the Instrument of Accession, ceding Kashmir to India on October 26.
Indian and Pakistani forces thus fought their first war over Kashmir in 1947-48. India referred the dispute to the United Nations on 1 January. In a resolution dated August 13, 1948, the UN asked Pakistan to remove its troops, after which India was also to withdraw the bulk of its forces.
Once this happened, a "free and fair" plebiscite was to be held to allow the Kashmiri people to decide their future.
India, having taken the issue to the UN, was confident of winning a plebiscite, since the most influential Kashmiri mass leader, Sheikh Abdullah, was firmly on its side. An emergency government was formed on October 30, 1948 with Sheikh Abdullah as the Prime Minister.
Pakistan ignored the UN mandate and continued fighting, holding on to the portion of Kashmir under its control. On January 1, 1949, a ceasefire was agreed, with 65 per cent of the territory under Indian control and the remainder with Pakistan.
The ceasefire was intended to be temporary but the Line of Control remains the de facto border between the two countries.
In 1957, Kashmir was formally incorporated into the Indian Union. It was granted a special status under Article 370 of India's constitution, which ensures, among other things, that non-Kashmiri Indians cannot buy property there.
Fighting broke out again in 1965, but a ceasefire was established that September. Indian Prime Minister, Lal Bhadur Shastri, and Pakistani President, M Ayub Khan, signed the Tashkent agreement on January 1, 1966.
They resolved to try to end the dispute, but the death of Mr Shastri and the rise of Gen Yahya Khan in Pakistan resulted in stalemate.
In 1971a third war, resulting in the formation of the independent nation of Bangladesh (formerly known as East Pakistan). A war had broken out in East Pakistan in March 1971, and soon India was faced with a million refugees.
India declared war on December 3, 1971 after Pakistani Air Force planes struck Indian airfields in the Western sector.
Two weeks later, the Indian army marched into Dhaka and the Pakistanis surrendered. In the Western sector the Indians managed to blockade the port city of Karachi and were 50 km into Pakistani territory when a ceasefire was reached.
In 1972 Indira Gandhi, the Indian prime minister, and Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, her Pakistani opposite number (and father of Benazir Bhutto, a later Pakistani premier), signed the Simla Agreement, which reiterated the promises made in Tashkent.
The two sides once again agreed to resolve the issue peacefully, as domestic issues dominated.
Both India and Pakistan had other important domestic problems which kept Kashmir on the back-burner. In 1975 Indira Gandhi declared a state of national emergency, but she was defeated in the 1978 general elections.
Zulfikar Ali Bhutto was overthrown and hanged in 1977; Pakistan reverted to military dictatorship under Gen Zia ul Haq.
The balance of influence had decisively tilted in Pakistan's favour by the late 1980s, with people's sympathy no longer with the Indian union as it had been in 1947-48 and 1965.
Mrs Gandhi's attempts to install puppet governments in state capitals, manipulating the democratic process in the state legislatures, deeply angered the Kashmiris.
The status quo was largely maintained until 1989 when pro-independence and pro-Pakistan guerrillas struck in the Indian Kashmir valley. They established a reign of terror and drove out almost all the Hindus from the valley before the Indian army moved in to flush them out. Meanwhile Indian and Pakistani troops regularly exchanged fire at the border.
Whereas in 1948 India took the Kashmir issue to the UN and was all for a plebiscite, by the 1990s it hid behind the Simla agreement and thwarted any attempts at UN or third-party mediation.
Over the decades the plebiscite advocated by India's great statesman Jawaharlal Nehru became a dirty word in New Delhi. These developments have led many to believe that Delhi has squandered the Kashmiri people's trust and allegiance.
India and Pakistan both tested nuclear devices in May 1998, and then in April 1999 test-fired missiles in efforts to perfect delivery systems for their nuclear weapons. Pakistan tested its Ghauri II missile four days after India's testing of its long-range (1,250 km) Agni II.
Although Pakistan claims that its missiles are an indigenous effort, in July 1999 Indian customs agents seized components shipped from North Korea which they claim were destined for Pakistan's missile programme.
Pakistan's later intermediate-range Ghauri III missile has a range of about 3,000 km.
When the Indian Prime Minister, Atal Behari Vajpayee, set out to Lahore by bus on February 20, 1999, inaugurating the four times a week Delhi-Lahore-Delhi bus service, the world felt that such a genuine effort at friendly neighbourhood relations would lower the tension along the Line of Control in Kashmir.
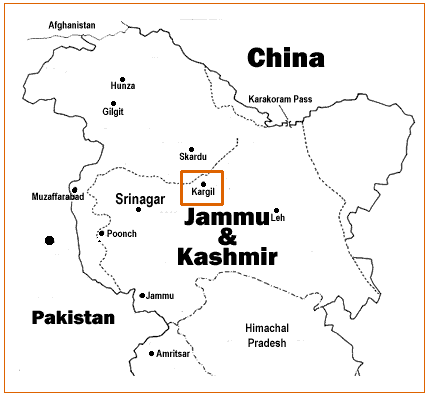
But, all hopes of diplomacy disappeared once the cross-LOC firing in Kargil began during the mid-1990s. The death toll , including both soldiers and civilians, was more than 30,000.
In the first week of August 1998 Indian and Pakistani troops exchanged artillery fire, described by locals as heavier than that of the 1948 and 1965 wars put together. An estimated 50,000 rounds of ammunition were expended and a large number of soldiers and civilians killed.
In the summer of 1999 hostility in Kargil went far beyond the now familiar annual exhange of artillery fire.
When India began patrolling the Kargil heights that summer, it found to its horror that many key posts vacated in the winter were occupied by infiltrators. A patrol was ambushed in the first week of May 1999. India belatedly realised the magnitude of the occupation - which was around 10 km deep and spanned almost 100 km of the LOC - and sent MiG fighters into action on May 26.
India contended that the infiltrators were trained and armed by Pakistan, and based in "Azad Kashmir" with the full knowledge of the Pakistani government - and that Afghan and other foreign mercenaries accompanied them.
Pakistan insisted that those involved were freedom fighters from Kashmir and that it was giving only moral support.
India ordered the jets not to stray into Pakistani territory; but those that did were shot down.
The conflict ended only after Bill Clinton, the US President, and Nawaz Sharif, Pakistan's Prime minister, met in Washington on July 4, 1999.
Meanwhile, the Indian Army had made significant advances, capturing vital territory on July 4. Despite the apparent efforts to mediate, the US maintained that it was not interfering in what India still claims to be a bilateral issue.
Pakistan withdrew its forces later that month. However, skirmishing continued, and in August India shot down a Pakistani reconnaissance plane, killing 16
The official number of Indian troops lost in Kargil was around 500, with almost double that number of "infiltrators" killed. Nevertheless, India did not declare war against Pakistan - instead, Mr Vajpayee ambigously announced a "war-like situation".
Yet this, by all accounts of soldiers and top Indian army officers involved, was a war in which India lost men engaged in hand-to-hand combat with Pakistani soldiers in the heights of Kargil - a war that could be compared with the one of 1948-49, which was limited to Kashmir, with the other border regions remaining peaceful.
Thus in 1999, in a war limited to one sector, India suffered casualities within its own territory. Despite much pressure from the military and the public, the government decided not to cross the LOC. Pakistan too suffered criticism at home for limiting its war to artillery fire across the LOC and shooting down Indian aircraft.
The fear of a full-scale war (with nuclear capability adding a deadly dimension), coupled with precarious economies and the knowledge of what international sanctions could do to them, may have prevailed in both countries.

The Kashmir dispute dates from 1947. The partition of the Indian sub-continent along religious lines led to the formation of India and Pakistan. However, there remained the problem of over 650 states, run by princes, existing within the two newly independent countries.
In theory, these princely states had the option of deciding
which country to join, or of remaining independent. In practice, the
restive population of each province proved decisive.
The people had been fighting for freedom from British rule,
and with their struggle about to bear fruit they were not willing to
let the princes fill the vacuum.
Although many princes wanted to be "independent" (which
would have meant hereditary monarchies and no hope for democracy) they
had to succumb to their people's protests which turned violent in many
provinces.
Because of its location, Kashmir could choose to join either
India or Pakistan. Maharaja Hari Singh, the ruler of Kashmir, was Hindu
while most of his subjects were Muslim. Unable to decide which nation
Kashmir should join, Hari Singh chose to remain neutral.
Maharaja Hari Singh signed the Instrument of Accession in October 1947 under which he acceded the State of Jammu and Kashmir to the Union of India.
But his hopes of remaining independent were dashed in October 1947, as Pakistan sent in Muslim tribesmen who were knocking at the gates of the capital Srinagar.
Hari Singh appealed to the Indian government for military assistance and fled to India. He signed the Instrument of Accession, ceding Kashmir to India on October 26.
Indian and Pakistani forces thus fought their first war over Kashmir in 1947-48. India referred the dispute to the United Nations on 1 January. In a resolution dated August 13, 1948, the UN asked Pakistan to remove its troops, after which India was also to withdraw the bulk of its forces.
Once this happened, a "free and fair" plebiscite was to be held to allow the Kashmiri people to decide their future.
India, having taken the issue to the UN, was confident of winning a plebiscite, since the most influential Kashmiri mass leader, Sheikh Abdullah, was firmly on its side. An emergency government was formed on October 30, 1948 with Sheikh Abdullah as the Prime Minister.
Pakistan ignored the UN mandate and continued fighting, holding on to the portion of Kashmir under its control. On January 1, 1949, a ceasefire was agreed, with 65 per cent of the territory under Indian control and the remainder with Pakistan.
The ceasefire was intended to be temporary but the Line of Control remains the de facto border between the two countries.
In 1957, Kashmir was formally incorporated into the Indian Union. It was granted a special status under Article 370 of India's constitution, which ensures, among other things, that non-Kashmiri Indians cannot buy property there.
Fighting broke out again in 1965, but a ceasefire was established that September. Indian Prime Minister, Lal Bhadur Shastri, and Pakistani President, M Ayub Khan, signed the Tashkent agreement on January 1, 1966.
They resolved to try to end the dispute, but the death of Mr Shastri and the rise of Gen Yahya Khan in Pakistan resulted in stalemate.
In 1971a third war, resulting in the formation of the independent nation of Bangladesh (formerly known as East Pakistan). A war had broken out in East Pakistan in March 1971, and soon India was faced with a million refugees.
India declared war on December 3, 1971 after Pakistani Air Force planes struck Indian airfields in the Western sector.
Two weeks later, the Indian army marched into Dhaka and the Pakistanis surrendered. In the Western sector the Indians managed to blockade the port city of Karachi and were 50 km into Pakistani territory when a ceasefire was reached.
In 1972 Indira Gandhi, the Indian prime minister, and Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, her Pakistani opposite number (and father of Benazir Bhutto, a later Pakistani premier), signed the Simla Agreement, which reiterated the promises made in Tashkent.
The two sides once again agreed to resolve the issue peacefully, as domestic issues dominated.
Both India and Pakistan had other important domestic problems which kept Kashmir on the back-burner. In 1975 Indira Gandhi declared a state of national emergency, but she was defeated in the 1978 general elections.
Zulfikar Ali Bhutto was overthrown and hanged in 1977; Pakistan reverted to military dictatorship under Gen Zia ul Haq.
The balance of influence had decisively tilted in Pakistan's favour by the late 1980s, with people's sympathy no longer with the Indian union as it had been in 1947-48 and 1965.
Mrs Gandhi's attempts to install puppet governments in state capitals, manipulating the democratic process in the state legislatures, deeply angered the Kashmiris.
The status quo was largely maintained until 1989 when pro-independence and pro-Pakistan guerrillas struck in the Indian Kashmir valley. They established a reign of terror and drove out almost all the Hindus from the valley before the Indian army moved in to flush them out. Meanwhile Indian and Pakistani troops regularly exchanged fire at the border.
Whereas in 1948 India took the Kashmir issue to the UN and was all for a plebiscite, by the 1990s it hid behind the Simla agreement and thwarted any attempts at UN or third-party mediation.
Over the decades the plebiscite advocated by India's great statesman Jawaharlal Nehru became a dirty word in New Delhi. These developments have led many to believe that Delhi has squandered the Kashmiri people's trust and allegiance.
India and Pakistan both tested nuclear devices in May 1998, and then in April 1999 test-fired missiles in efforts to perfect delivery systems for their nuclear weapons. Pakistan tested its Ghauri II missile four days after India's testing of its long-range (1,250 km) Agni II.
Although Pakistan claims that its missiles are an indigenous effort, in July 1999 Indian customs agents seized components shipped from North Korea which they claim were destined for Pakistan's missile programme.
Pakistan's later intermediate-range Ghauri III missile has a range of about 3,000 km.
When the Indian Prime Minister, Atal Behari Vajpayee, set out to Lahore by bus on February 20, 1999, inaugurating the four times a week Delhi-Lahore-Delhi bus service, the world felt that such a genuine effort at friendly neighbourhood relations would lower the tension along the Line of Control in Kashmir.

But, all hopes of diplomacy disappeared once the cross-LOC firing in Kargil began during the mid-1990s. The death toll , including both soldiers and civilians, was more than 30,000.
In the first week of August 1998 Indian and Pakistani troops exchanged artillery fire, described by locals as heavier than that of the 1948 and 1965 wars put together. An estimated 50,000 rounds of ammunition were expended and a large number of soldiers and civilians killed.
In the summer of 1999 hostility in Kargil went far beyond the now familiar annual exhange of artillery fire.
When India began patrolling the Kargil heights that summer, it found to its horror that many key posts vacated in the winter were occupied by infiltrators. A patrol was ambushed in the first week of May 1999. India belatedly realised the magnitude of the occupation - which was around 10 km deep and spanned almost 100 km of the LOC - and sent MiG fighters into action on May 26.
India contended that the infiltrators were trained and armed by Pakistan, and based in "Azad Kashmir" with the full knowledge of the Pakistani government - and that Afghan and other foreign mercenaries accompanied them.
Pakistan insisted that those involved were freedom fighters from Kashmir and that it was giving only moral support.
India ordered the jets not to stray into Pakistani territory; but those that did were shot down.
The conflict ended only after Bill Clinton, the US President, and Nawaz Sharif, Pakistan's Prime minister, met in Washington on July 4, 1999.
Meanwhile, the Indian Army had made significant advances, capturing vital territory on July 4. Despite the apparent efforts to mediate, the US maintained that it was not interfering in what India still claims to be a bilateral issue.
Pakistan withdrew its forces later that month. However, skirmishing continued, and in August India shot down a Pakistani reconnaissance plane, killing 16
The official number of Indian troops lost in Kargil was around 500, with almost double that number of "infiltrators" killed. Nevertheless, India did not declare war against Pakistan - instead, Mr Vajpayee ambigously announced a "war-like situation".
Yet this, by all accounts of soldiers and top Indian army officers involved, was a war in which India lost men engaged in hand-to-hand combat with Pakistani soldiers in the heights of Kargil - a war that could be compared with the one of 1948-49, which was limited to Kashmir, with the other border regions remaining peaceful.
Thus in 1999, in a war limited to one sector, India suffered casualities within its own territory. Despite much pressure from the military and the public, the government decided not to cross the LOC. Pakistan too suffered criticism at home for limiting its war to artillery fire across the LOC and shooting down Indian aircraft.
The fear of a full-scale war (with nuclear capability adding a deadly dimension), coupled with precarious economies and the knowledge of what international sanctions could do to them, may have prevailed in both countries.